Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDPs)
Most knowledge about proteins concerns structured proteins with specific functions. However, most proteins don’t have a particular or unique structure, and this doesn’t imply a lack of function. This makes IDPs incredibly interesting. The formation of protein-protein interactions underlies how proteins evolve to perform different functions.

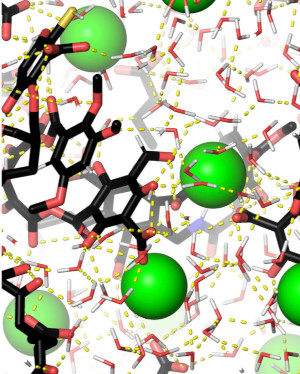
Soil Organic Matter (SOM)
Most of the soils have a clear, dark/brown-colored layer. This layer comprises hundreds of years of decomposition of various organic compounds, known as Soil Organic Matter (SOM). SOM is composed of heterogeneous, dispersed organic compounds in association with the soil mineral matrix. This mineral matrix presents an oxidative environment with various ionic species. The variety of organic compounds is characterized by compounds rich in aromatic rings and carboxyl groups. In this sea of possibilities, I have tried to understand the interactions of these compounds.
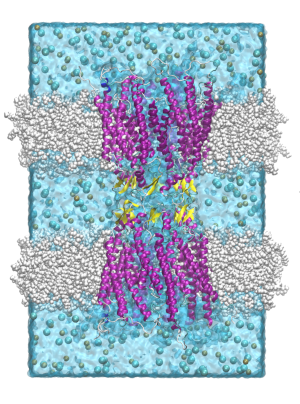
Ionic channels
The cells have a membrane barrier. The connection to the environment occurs through channels; those specified to transport ionic species are called ionic channels. However, cells can communicate with other cells. This is done in our cells through Gap Junction Channels (GJCs)—a novel channel between cells that permits electrical synapses, or fast interactions. The complexity of these channels stems from the multiple interactions among their subunits and from how they filter positive ions.
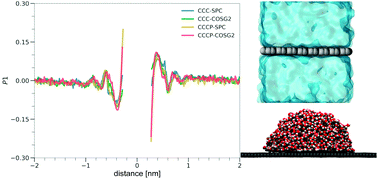
Graphene interactions
With the increasing use of nanoparticles, understanding their interactions with our bodies becomes necessary. For starters, we need to know how simple molecules interact with graphene. The first and most important on the list is water. The water-graphene interaction depends on the graphene layer’s polarizability and the water molecules’ polarisability. These interactions can be investigated using molecular dynamics simulations that account for the molecules’ polarizability.
Structural bioinformatics
The structure and function of proteins depend on their amino acid compositions. The close interaction between two amino acids can be correlated with the rate of mutation between them during evolution. These changes can be observed through bioinformatic analyses across multiple sequences.